|
|
|||||
| intern | ||||||
|
|
||||||
| ||||||||||
2.1 the grating
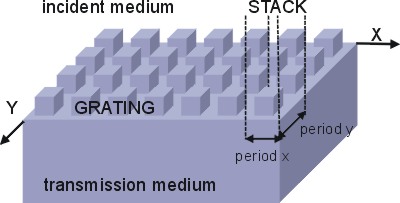 This is a 2D grating. It has a grating period in x-direction, and a grating period in y-direction. Those are infinitly repeated. The number of layers in z-direction however is finite, starting with an incidence medium and ending with the transmission medium. A 1D grating looks the same... but without a y-period. Now, this 2D anti-tank grating exists of seperated concrete blocks. One cell of that grid is a stack. A stack is a 3D pile which holds the air (incident medium) and the soil (transmission medium) and everything in between.
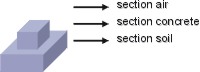
The stack excist of distinct sections. Those are 2D structures,
with witdh =
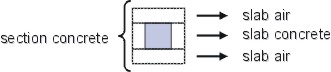
Each section is constructed with 1D slabs.
They have a width of
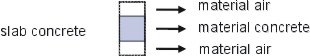 A material has no dimension, it only holds a refractive index. That index can be complex, a positive imaginary part means gain, negative means losses.
Now we start talking about refractive index... concrete is not the most ideal medium of course, but our financial situation doesn't allow us costly building projects at the moment, so we recycled that anti-tank stuff from WWII. Sorry. This document was generated by Lieven Vanholme on June, 10 2003 using texi2html. |